Discover a strategic approach to wealth accumulation with dollar-cost averaging (DCA), an investment technique that can assist you in attaining your financial objectives. Dollar-cost averaging involves regularly investing a fixed amount of funds into a specific investment, regardless of the prevailing market conditions. This method lets you capitalize on market fluctuations and potentially decrease your average share cost over time. By spreading your investments across an extended duration, you can mitigate the hazards associated with timing the market and potentially benefit from the compounding effect. Regardless of your investment experience, implementing dollar-cost averaging can revolutionize your path to wealth creation. We will discuss dollar-cost averaging, its mechanics, and the compelling reasons to consider adopting this strategy. Prepare to unlock the full potential of your investments and pave your way to financial triumph with dollar-cost averaging.
How Does Dollar-Cost Averaging Work?
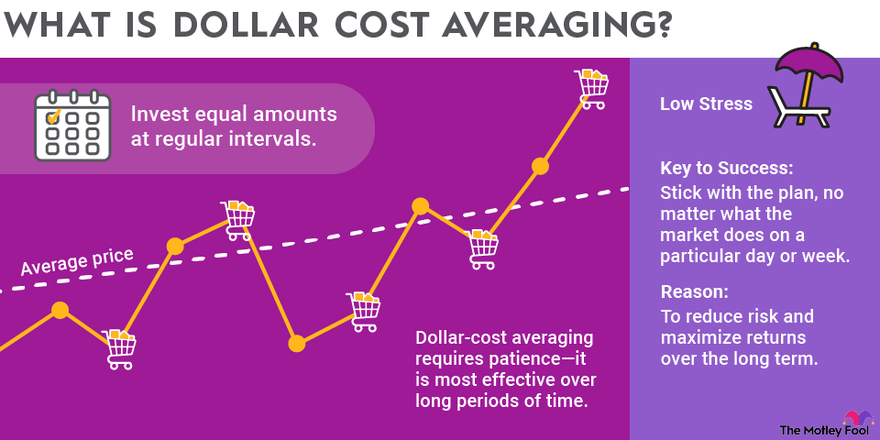
Discovering the methodology behind dollar-cost averaging can provide valuable insights for strategic investing. Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where you possess a sum of $1,000 to allocate toward a specific stock. Rather than investing the entire amount in one go, a more prudent approach involves distributing $100 per month over a span of ten months.
To illustrate, let’s delve into the practical implications. In the initial month, the stock is valued at $10 per share, allowing you to acquire 10 shares. Subsequently, in the second month, the stock price experiences a decline to $8 per share, enabling you to procure 12.5 shares. As the third month rolls around, the stock value rebounds to $12 per share, facilitating the purchase of 8.33 shares. This pattern continues over the course of subsequent months.
By consistently investing a predetermined sum, the investor capitalizes on favorable opportunities when prices are low and secures fewer shares during high prices. Over time, this strategic approach can effectively reduce the average cost per share. Moreover, spreading the investment across an extended timeframe mitigates the potential risk of making a substantial investment at an inopportune moment.
Advantages of Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging, an investment approach embraced by both seasoned and novice investors, offers a multitude of benefits worth exploring.
First and foremost, this strategy obviates the necessity of market timing. Predicting market trends remains arduous, even for experienced investors who grapple with consistent accuracy. By adhering to regular investment intervals, the focus shifts to the enduring growth potential of investments, sidestepping forecasting challenges.
Secondly, dollar-cost averaging can lessen the impact of immediate market volatility. It’s common knowledge that financial markets often behave unpredictably, subject to rapid fluctuations. By steadfastly investing over extended periods, the effects of these market swings are smoothed out, potentially capitalizing on the market’s upward trajectory.
Thirdly, dollar-cost averaging can harness the power of compounding. Regular investments allow ample time for wealth accumulation and compounding. As time progresses, this compounding effect can markedly augment one’s financial prosperity and expedite the realization of financial aspirations.
Credit: fool.com
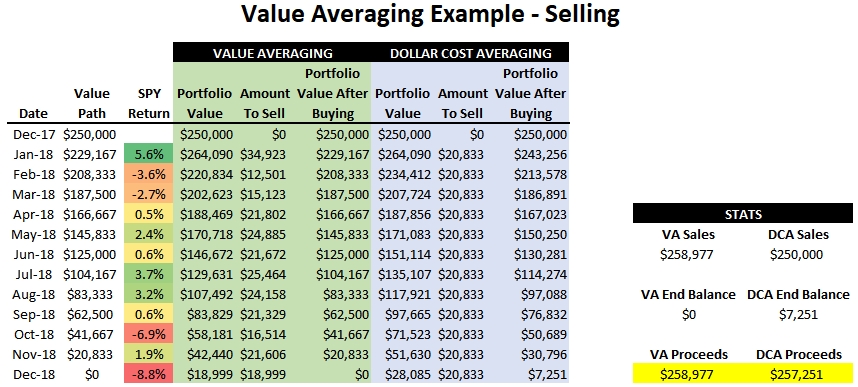
Comparing Dollar-Cost Averaging and Lump Sum Investing
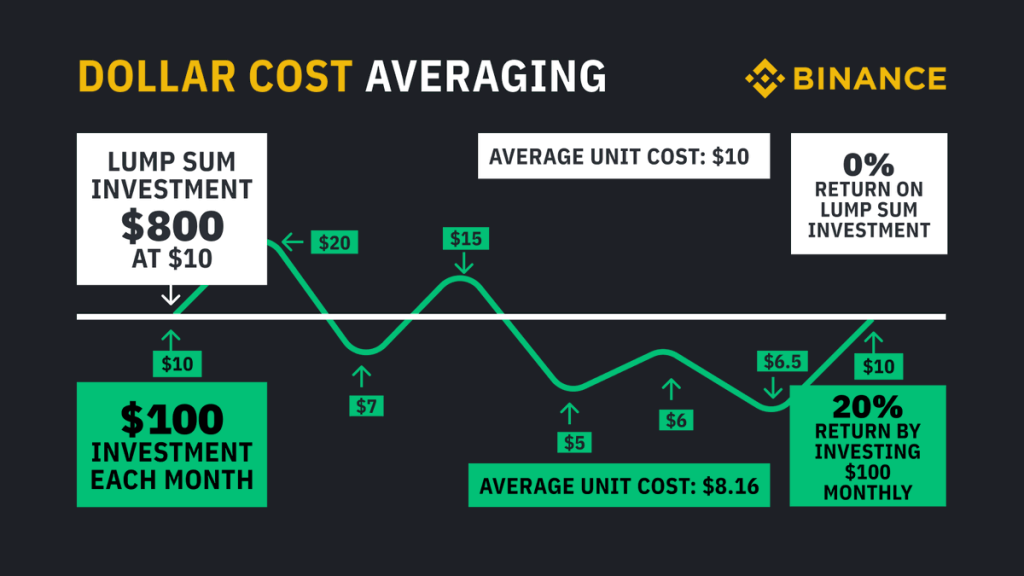
When it comes to investment strategies, a common query arises regarding the distinction between dollar-cost averaging and lump-sum investing. While both approaches have their merits, their methods and risk profiles vary.
Dollar-cost averaging adopts a cautious stance, distributing investments over an extended period. By using this strategy, you can avoid making substantial investments at an inopportune time. By investing gradually, you can mitigate short-term market fluctuations and potentially benefit from lower prices.
On the other hand, lump sum investing can be advantageous if you possess a considerable sum of available funds and believe that the market is undervalued or poised for substantial growth. By investing all at once, you have the potential to capture immediate gains if the market performs favorably. However, this approach also exposes you to the risk of making a substantial investment at an unfavorable time, particularly if the market experiences a downturn shortly after your investment.
Ultimately, the decision between dollar-cost averaging and lump sum investing hinges on your unique circumstances, risk tolerance, and market outlook. It is crucial to carefully contemplate your financial objectives and seek guidance from a financial advisor prior to making any investment choices.
Guide to Successfully Implementing Dollar-Cost Averaging
Implementing dollar-cost averaging, a proven investment strategy can be accomplished through the following steps:
- Identify your investment objectives, risk tolerance, and timeframe. You can then determine the suitable investment amount and the types of investments that align with your objectives.
- Investing options: Choose investment vehicles compatible with your goals and risk appetite. The holdings may include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or a combination.
- Plan your investment amounts and intervals: Decide how much money you will consistently invest and how often. This could involve allocating a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of your income.
- Streamline your investment process: Consider automating your investment activities to foster consistency and commitment. Explore setting up automated transfers or contributions to your investment account, eliminating the need for manual intervention and ensuring regular investments.
- Monitor and adapt as necessary: Regularly assess the performance of your investments and make any required adjustments to your investment strategy. This might entail rebalancing your portfolio, modifying investment amounts, or adjusting investment vehicles in response to prevailing market conditions.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively execute dollar-cost averaging, enhancing your prospects for long-term investment prosperity.
Credit: twitter.com
Dispelling Common Misconceptions about Dollar-Cost Averaging
Despite its widely acknowledged effectiveness as an investment strategy, there are several misconceptions surrounding dollar-cost averaging that merit clarification:
- “Dollar-cost averaging ensures guaranteed profits“: No, dollar-cost averaging cannot guarantee profit or prevent loss. It is an investment model that aims to lower the average cost per share and lessen the impact of short-term volatility. Investment performance can still be affected by various factors, including market conditions and economic variables.
- “Dollar-cost averaging exclusively caters to beginners“: It suits investors at all experience levels. It offers advantages such as risk mitigation, long-term growth potential, and the compounding effect. As such, it can be effectively employed by both novice and seasoned investors alike.
- “Dollar-cost averaging solely pertains to stocks“: While dollar-cost averaging is commonly associated with stock investments, its application extends beyond this asset class. It can be effectively utilized in purchasing bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, and other investment vehicles.
Acquiring a comprehensive understanding of dollar-cost averaging and dispelling these prevalent misconceptions is vital. By doing so, you can make well-informed investment decisions and optimize the advantages provided by this strategy.
Important Considerations and Risks Associated with Dollar-Cost Averaging
When engaging in dollar-cost averaging, it is crucial to take into account the following factors to ensure an informed investment strategy:
- “Missed potential gains”: The fixed investment amounts at regular intervals may result in missed opportunities for significant profits if the market experiences substantial upswings. This becomes particularly relevant during periods of rapid market growth.
- “Fees and expenses”: Depending on the chosen investment platform and vehicle, there might be associated costs for each investment transaction. These expenses can reduce your overall returns, primarily when investing smaller amounts regularly.
- “Market downturns”: It’s important to recognize that dollar-cost averaging does not shield you from market downturns or guarantee protection against losses. Although the strategy can help alleviate the impact of short-term market volatility, it does not eliminate the risk of investing during an extended market decline.
- “Choosing suitable investments”: The success of dollar-cost averaging hinges on selecting quality investments that align with your specific goals and risk tolerance. Conducting thorough research is crucial to make well-informed investment decisions.
- “Emotional resilience”: Successful execution of dollar-cost averaging requires discipline and a long-term perspective. It can be challenging to adhere to the strategy when faced with market uncertainties or emotional decision-making. Stay focused on your investment objectives and don’t let short-term market fluctuations sway you.
Your investment strategy will be more effective if you understand these risks and considerations.
Credit: eversightwealth.com
Dollar-Cost Averaging with Different Investment Vehicles
The strategy of dollar-cost averaging can be effectively utilized across a range of investment vehicles, such as equities, fixed-income securities, pooled investment funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and other options. Each investment vehicle possesses unique features and considerations pertinent to implementing the dollar-cost averaging approach.
You can gradually construct a well-diversified portfolio when applying dollar-cost averaging to stocks. By consistently investing in various stocks, you distribute your risk and potentially reap benefits from the growth of multiple companies.
In contrast, bonds offer a more cautious investment avenue. Dollar-cost averaging with bonds can provide a regular income stream and safeguard your capital. Regular investments in bonds allow you to capitalize on fluctuations in interest rates and potentially enhance your overall returns.
Mutual funds and ETFs serve as popular investment vehicles that provide diversification and professional management. By employing dollar-cost averaging with these funds, you can gain exposure to various assets and industries, mitigating the risks of selecting individual stocks.
It is crucial to consider the distinct characteristics of each investment vehicle and evaluate how they align with your goals and risk tolerance. Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can aid you in determining the most appropriate investment vehicles for implementing your dollar-cost averaging strategy.
Conclusion
Investment enthusiasts seeking a reliable and enduring approach to wealth accumulation should acquaint themselves with the concept of dollar-cost averaging. When diligently practiced, this investment strategy can yield significant benefits over time. By consistently investing a predetermined sum of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions, individuals can capitalize on market fluctuations and potentially diminish their average cost per share. The advantages of this strategy encompass risk reduction, long-term growth prospects, and the compounding effect.
While it is prudent to acknowledge the potential risks and considerations associated with dollar-cost averaging, it is worth noting that this strategy maintains its status as a widely favored and productive approach for both novice and seasoned investors. By comprehending the underlying principles, correctly implementing the process, and maintaining discipline, investors can unlock the full potential of their investments, thus paving the way for financial triumph.
If you aspire to pursue a prudent and effective means of building wealth, consider incorporating the practice of dollar-cost averaging into your investment strategy. Begin your journey toward financial success today by embracing this intelligent approach!






Add Comment