The transition into retirement is often seen as a time of relaxation and freedom, serving as a well-deserved break after years of diligent work. However, this phase also introduces unique financial challenges requiring thoughtful planning and prudent decision-making. This is where the risk management in retirement concept becomes crucial.
Risk management in retirement involves systematically recognizing, evaluating, and devising strategies to address potential financial uncertainties that may impact your retirement savings and income. It entails making well-informed choices to safeguard your nest egg from unpredictable factors like market fluctuations, inflation, and longevity risks.
Emphasizing the significance of risk management is paramount. With the rise in life expectancy, retirement spans a more extended period, necessitating that your savings endure for longer. Additionally, the unpredictable nature of the market, interest rates, and inflation can significantly influence the value of your retirement funds.
Furthermore, retirement signifies a shift from accumulating income to distributing it, presenting a distinct set of risks. Consequently, implementing effective strategies to manage these risks becomes vital to ensure a consistent income stream throughout retirement and uphold your diligently cultivated lifestyle.
Retirement risk management encompasses preserving your wealth and creating a safety net that enables you to relish your golden years without worry. Its essence lies in guaranteeing that your retirement embodies the rewarding and fulfilling period it intends to be.
Understanding the Risks in Retirement
As we progress towards retirement, understanding the potential risks that could jeopardize our financial well-being becomes increasingly vital. This intricate process, known as retirement risk management, encompasses identifying and adopting measures to mitigate these risks. In the following discussion, we will delve into the various categories of risks encountered after retirement and explore their potential influence on retirement planning.
Post-Retirement Risk Factors
Retirement initiates a substantial shift in income sources, replacing regular paychecks with reliance on social security, pensions, annuities, and personal savings. However, these income streams are susceptible to various risks, including market fluctuations, interest rate modifications, inflation, and liquidity constraints. Grasping the nature of these risks constitutes the primary step toward implementing an effective retirement risk management strategy.
Market Volatility Risk
Market volatility, often referred to as systematic risk, denotes the potential for investors to suffer losses due to factors influencing the overall performance of financial markets. Economic circumstances such as recessions, political instability, or national events like elections can trigger declines in investment values. Retirees who invest a large portion of their retirement savings in the stock market face this risk. A market downturn can profoundly impact the value of these investments, consequently affecting the retiree’s income stream.
Interest Rate Fluctuation Risk
Interest rate fluctuation risk encompasses the possibility of an investment’s value diminishing due to increased interest rates. Bonds are especially vulnerable to this risk, as their prices typically decline when interest rates rise and vice versa. Retirees who allocate a significant portion of their investment portfolio to bonds as a safer alternative to stocks may face potential devaluation if interest rates abruptly surge. This devaluation can impede their retirement income, mainly if they intend to sell these bonds to cover retirement expenses.
Inflation Risk
Inflationary risk denotes the hazard associated with the mounting cost of living, which is essential in retirement planning. Inflation can erode retirement savings over time. Failure to maintain investments that outpace inflation may result in inadequate income from savings to cover living expenses during retirement. This risk is particularly relevant for those who adopt overly conservative investment strategies, as such approaches may not generate returns that outperform inflation.
Liquidity Risk
Lastly, liquidity constraint risk refers to the possibility of being unable to swiftly convert an investment into cash without incurring significant losses in value. This risk becomes particularly pertinent for retirees who may require immediate access to savings for unforeseen expenses. If a substantial portion of retirement savings is tied up in investments that cannot be quickly sold or cashed in, an unexpected expense can lead to financial strain.
To conclude, a comprehensive comprehension of these risks is integral to effective retirement risk management. By acknowledging these potential challenges, retirees can make informed decisions regarding their retirement savings and investment strategies, ensuring a financially secure and enjoyable retirement period.
Credit: wallstreetmojo.com
Effective Approaches to Mitigate Retirement Risks
Planning for retirement is a crucial milestone that necessitates thoughtful consideration and prudent financial management. One of the critical components of retirement planning involves effectively managing potential risks. This section will explore four essential strategies that can significantly contribute to risk mitigation during retirement: diversification, asset allocation, regular portfolio assessment and adjustment, and dollar cost averaging.
Diversification
Diversification is a fundamental technique in risk management during retirement. Its principle involves spreading investments across various asset classes to minimize exposure to individual assets or risks, thus avoiding overreliance on a single source.
- Diversification safeguards against underperforming sectors by balancing them with better-performing ones.
- Diversifying investments across different asset types is essential, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents.
- Within each asset class, it is also advisable to diversify further. For example, consider a blend of domestic, international, growth, and value stocks when allocating stocks.
- While diversification does not guarantee profits or eliminate losses, it effectively helps manage risk and stabilize returns over time.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is another pivotal strategy for risk management during retirement. It involves dividing an investment portfolio among various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and cash or cash equivalents.
- The allocation of assets should align with one’s financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment timeframe.
- Generally, a higher risk tolerance leads to a greater inclination toward stocks within the portfolio. Conversely, for those with a lower tolerance for risk, a focus on bonds and cash may be more suitable.
- As retirement approaches, gradually shifting towards a more conservative asset allocation is advisable to preserve capital. However, maintaining exposure to growth-oriented assets like stocks can help the portfolio keep pace with inflation.
Regular Portfolio Assessment and Adjustment
Regularly assessing and adjusting one’s portfolio is a proactive approach to risk management during retirement. This strategy involves periodic reviews to ensure the portfolio meets financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Market fluctuations over time can cause a portfolio to deviate from its original asset allocation. Regular assessments help identify such deviations.
- Rebalancing entails making necessary adjustments to realign the portfolio with the desired asset allocation. This might involve selling certain assets and acquiring others.
- Regular portfolio maintenance assists in managing risk by ensuring that investments continuously align with retirement goals and risk tolerance.
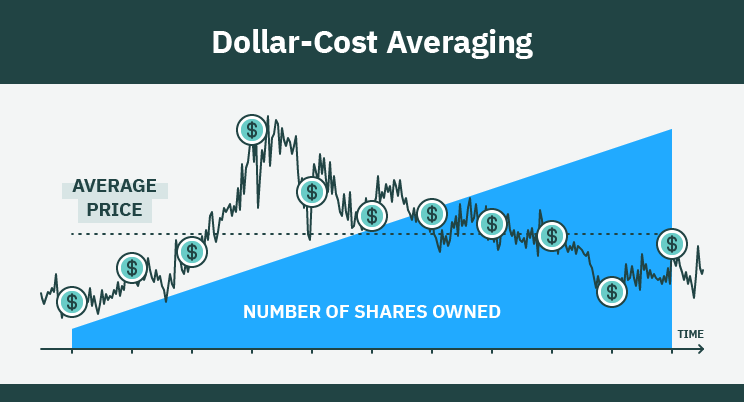
Dollar Cost Averaging
An effective method of investing is dollar-cost averaging (DCA), which involves investing a fixed amount at regular intervals, regardless of the investment’s current price. This method proves particularly beneficial in managing investment risk within a retirement portfolio.
- DCA eliminates emotional decision-making by ensuring consistent investments irrespective of market conditions.
- It mitigates the impact of market volatility by spreading out investment purchases. When prices are low, the fixed investment amount purchases more shares, while fewer shares are bought when prices are high.
- Over time, this strategy could result in a lower average cost per share than a lump sum investment made at a single time.
In conclusion, risk management during retirement encompasses a multifaceted process that involves diversification, asset allocation, regular portfolio assessment and adjustment, and dollar cost averaging. By comprehending and implementing these strategies, individuals can adeptly navigate the financial risks associated with retirement and work towards their retirement goals.
Credit: tokenist.com
The Significance of Personal Risk Tolerance in Risk Management
When managing risks during retirement, having a clear grasp of your personal risk tolerance becomes paramount. It verifies the level of uncertainty you are ready to handle in return for potential gains.
Importance of Personal Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance determines how much you are willing to take on risk. It shapes your investment strategy and determines your retirement income.
- Understanding your risk tolerance aids in making investment choices that align with your financial goals and comfort level.
- You must balance risk and reward within your retirement portfolio.
- By having a well-aligned risk tolerance, you can better weather market volatility and reduce the likelihood of impulsive decisions that might jeopardize your retirement savings.
Factors Influencing Personal Risk Tolerance
Several factors influence your risk tolerance, including your financial circumstances, investment timeline, and disposition.
- Financial circumstances: Those with a secure financial safety net tend to be more at ease with assuming risk.
- Investment timeline: A longer investment timeline generally allows for greater risk acceptance, as more time is available to recover from potential losses.
- Personal disposition: Each individual has a unique level of risk aversion. Your comfort level with uncertainty significantly shapes your risk tolerance.
How to Determine Your Personal Risk Tolerance
Determining your risk tolerance involves self-reflection and sometimes seeking guidance from a financial expert.
- Reflect upon your financial goals and evaluate the extent of risk you are willing to undertake to achieve them.
- Contemplate hypothetical scenarios of market downturns and assess your likely responses. Would you panic and sell or maintain your course?
- Utilize online risk tolerance questionnaires. These tools offer a rough estimate of your risk tolerance based on your reactions to different scenarios.
- Discuss your risk tolerance with a financial advisor and assist in aligning it with your overall retirement plan.
In conclusion, comprehending your personal risk tolerance is vital to retirement risk management. It ensures that your investment strategy harmonizes with your comfort level, financial aspirations, and investment timeline, enabling you to navigate market fluctuations and strive for a secure retirement future.
Conclusion
Retirement marks a significant milestone in life, introducing a distinct set of financial considerations. Managing potential risks during retirement holds utmost importance, necessitating a comprehensive approach. Effectively addressing these risks safeguards your hard-earned savings from market fluctuations, inflation, and interest rate changes.
Throughout this article, we have delved into strategies to mitigate these risks substantially. Techniques such as diversifying your portfolio, allocating assets strategically, and regularly rebalancing your investments play a crucial role. Additionally, comprehending your personal risk tolerance and utilizing tools like dollar cost averaging can further bolster the resilience of your retirement plan.
Nonetheless, navigating the intricate landscape of risk management in retirement can be daunting. This is where the expertise of a financial professional becomes invaluable. By seeking guidance from a financial advisor, you can access personalized advice tailored to your unique financial objectives and risk tolerance. Their insights empower you to make informed decisions regarding your retirement income.
Risk management is not only an option. It’s an essential part of securing a prosperous retirement. The key to financial security and peace of mind in your golden years is to assess potential risks, implement effective strategies, and, if necessary, seek professional guidance. Make sure your retirement is comfortable and secure by taking responsibility today.





