In one’s life, it is crucial to consider both the present and the future. An essential aspect of this consideration involves making retirement plans. Retirement planning encompasses envisioning life after retirement and acquiring the financial stability necessary to sustain one’s desired lifestyle. This comprehensive article offers an extensive guide on strategies for retirement planning, providing valuable insights to aid you in achieving a secure and prosperous retirement.
Retirement planning extends beyond mere savings. It entails strategic investments, maximizing contributions, portfolio diversification, and using tax-advantaged retirement accounts. The process involves comprehending your financial objectives and aligning your savings and investments accordingly to fulfill those aspirations.
Within this article, we will explore the significance of retirement planning, delve into various effective strategies, discuss the selection of appropriate retirement plans, and examine investment approaches specifically tailored for retirement. Additionally, we will address frequently asked questions surrounding retirement planning.
Regardless of whether you are at the onset of your career or nearing retirement age, initiating the planning process is never too early or too late. Join us on this enlightening journey to comprehensively understand retirement planning strategies, ensuring a financially sound and comfortable retirement.
Understanding Retirement Planning
The process of retirement planning plays a critical role in effective financial management, emphasizing the establishment and supervision of a retirement fund. Its goal is to determine retirement income objectives and devise necessary measures to accomplish them. Retirement planning encompasses identifying income sources, estimating expenses, implementing a savings regimen, and prudent management of assets and risks.
The significance of adequately addressing the matter of retirement planning cannot be overstated. This strategic approach ensures financial security and stability during post-employment when a consistent income is no longer obtained. By engaging in proper retirement planning, individuals can sustain their desired lifestyle, effectively handle healthcare expenditures, and cope with unexpected expenses that may emerge in their retirement years. It facilitates the creation of a protective cushion that enables retirees to relish their post-work period without encountering financial strain.
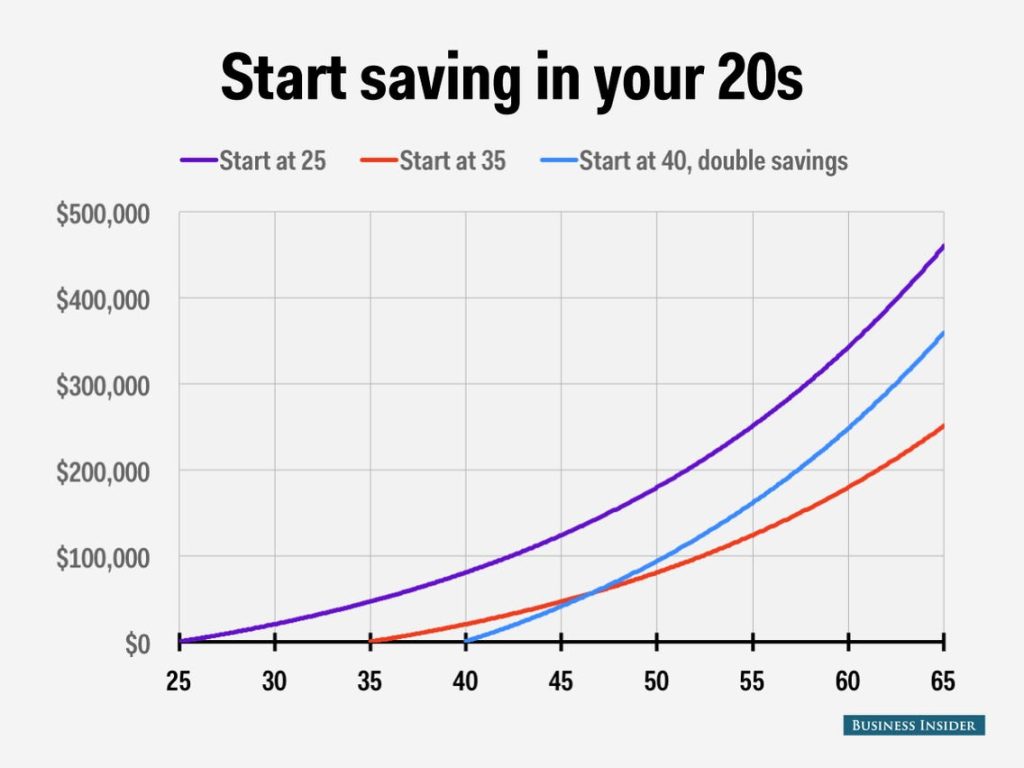
The question arises: when is the ideal time to commence retirement planning? The answer lies in initiating this process as early as feasible. By beginning retirement planning at the earliest opportunity, individuals afford more significant time for saving and investment. Early engagement is the chance to harness the power of compounding, wherein earnings generate further earnings over time, leading to exponential growth.
However, even those who find themselves beginning the process later in life should not despair. Every bit of savings accumulates and counts towards the ultimate goal. It is never too late to implement effective strategies for retirement planning. One must remember that the objective is to build a retirement fund that can adequately sustain one’s chosen lifestyle and facilitate the achievement of retirement aspirations.
To summarize, comprehending the nuances of retirement planning represents the initial stride toward safeguarding one’s financial future. The process extends beyond the mere act of saving money; it revolves around making astute decisions that culminate in creating a comfortable nest egg for the retirement years.
The following are key takeaways to consider:
- Retirement planning encompasses a process through which individuals identify retirement income objectives and delineate steps to achieve them.
- The essence of retirement planning lies in its capacity to furnish financial security throughout the retirement phase.
- Initiating retirement planning at the earliest juncture permits the maximization of savings and capitalizes on the power of compounding.
- Regardless of the starting point, any amount of savings holds significance, and commencing retirement planning is always a viable option.
Ultimately, the key to successful retirement planning is to begin the process early, maintain consistent savings contributions, and make wise investment decisions.
Credit: businessinsider.com
Retirement Planning Strategies
Preparing for retirement is a fundamental component of prudent financial management. It encompasses an array of methods devised to facilitate the realization of your financial objectives and uphold your desired lifestyle during your retirement years. Below are several crucial strategies for strategic retirement planning that can serve as your guiding principles on this journey.
Strategy 1: Start Early
The foremost and arguably most critical strategy involves commencing the process early. Initiating your retirement planning as soon as possible allows your funds to grow significantly. This strategy capitalizes on the principle of compounding, enabling your savings to multiply over an extended period.
Strategy 2: Diversify Your Investments
The principle of investment diversification assumes paramount importance in retirement planning. To mitigate risks, investments are spread among a range of assets, such as equities, bonds, and mutual funds. Diversification acts as a protective measure, ensuring that gains from one investment offset losses in another, thereby safeguarding your retirement savings.
Strategy 3: Maximize Your Contributions
Another indispensable strategy involves maximizing your contributions to your retirement accounts. Be it a 401(k), an IRA, or other similar accounts, aim to contribute as much as feasible. Numerous employers offer matching contributions to 401(k) plans, which can significantly augment your retirement savings.
Strategy 4: Consider Tax-Advantaged Retirement Accounts
Lastly, consider directing your investments toward tax-advantaged retirement accounts. These specialized accounts, like 401(k)s and IRAs, provide tax benefits that can optimize the growth of your savings. These advantages encompass tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, or tax-free withdrawals during retirement, contingent upon the account type.
Strategy 5: Plan for Healthcare Costs
Healthcare expenses represent a substantial portion of retirement outlays. As individuals age, the demand for medical care typically rises, accompanied by increased associated costs. Consequently, healthcare expenses must be part of your retirement plan. Explore alternatives such as Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Long-Term Care Insurance. Moreover, you need to know what Medicare offers and what it excludes. Bear in mind that planning in advance for healthcare costs can safeguard your retirement savings against unforeseen medical expenditures.
Strategy 6: Create a Post-Retirement Budget
Developing a budget specifically designed for the post-retirement period is a pivotal strategy in retirement planning. This budget should reflect your desired retirement lifestyle and account for all potential sources of income, such as Social Security benefits, retirement accounts, and potential part-time employment.
Here is a straightforward approach to accomplish this:
- Enumerate all anticipated income sources.
- Deduct the estimated tax payments.
- Enumerate your projected regular expenses, encompassing housing, utilities, food, transportation, and healthcare.
- Remember to include recreational activities and travel expenses, which are integral to enjoying your retirement.
- Lastly, allocate funds for potential unexpected expenses.
By creating a realistic post-retirement budget, you can better understand the amount you need to save presently to relish your desired retirement lifestyle.
Incorporating these strategies into your retirement planning endeavors can ensure that you are financially prepared for retirement. Remember that initiating the planning process early on and regularly reviewing your plan are the key factors contributing to successful retirement planning.
Selecting an Optimal Retirement Plan
When devising effective strategies for securing your financial future post-employment, one of the most critical choices you’ll face involves selecting a suitable retirement plan. This decision significantly impacts your long-term economic stability during your golden years. Various retirement accounts are available, each possessing distinctive attributes and advantages. Let’s explore an overview of diverse retirement plans and gain insights on selecting the most advantageous one for your specific circumstances.
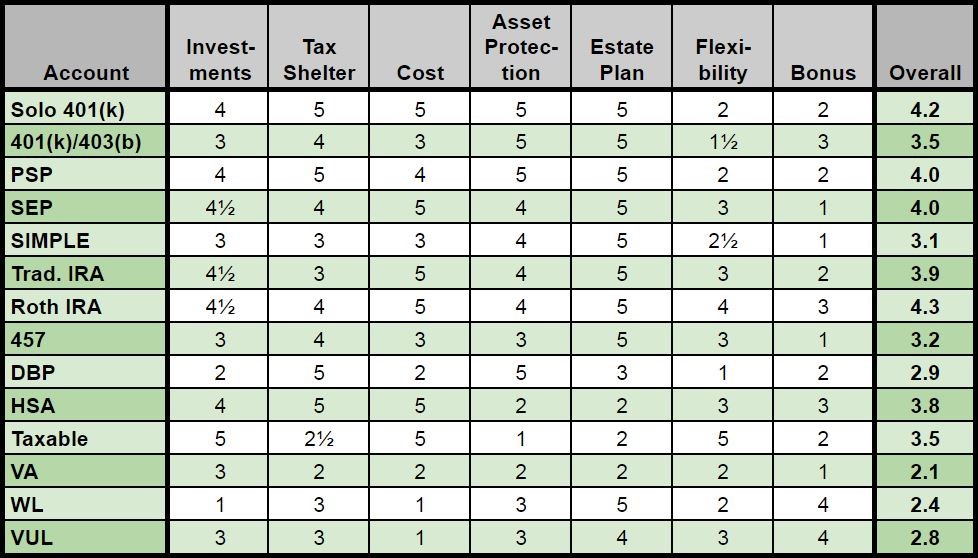
- 401(k) Plans: These retirement accounts are provided by employers and facilitate employees’ contributions from their pre-tax income, which can grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. Some employers even offer matching grants, resulting in free money towards your retirement savings.
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA): An IRA is a retirement account with tax advantages that you open independently. Two primary types exist: Traditional IRA and Roth IRA. Traditional IRA contributions are tax deductible, and investment earnings grow tax-deferred until withdrawal in retirement. In contrast, Roth IRA contributions are made using after-tax funds, but withdrawals during retirement are tax-free.
- Roth 401(k) Plans: The Roth 401(k) combines elements of the 401(k) and the Roth IRA. Contributions are made with after-tax income, while withdrawals during retirement are tax-free. Similar to a regular 401(k), employers typically offer this plan.
The choice of the most suitable retirement plan depends on several factors. Make sure you consider your income level, tax situation, 401(k) match, and tax preference.
Remember, there is no universal solution regarding retirement planning strategies. A financial advisor can assess your situation carefully and help you make an informed decision. A solid retirement plan establishes a secure financial future.
Credit: whitecoatinvestor.com
Investment Strategies for Retirement
Multiple routes exist for channeling retirement savings, each with distinct advantages and risks. Below are some commonly utilized alternatives:
- Stocks: By investing in individual stocks, individuals can potentially yield substantial returns. However, such investments also carry heightened risk, necessitating the diversification of one’s stock portfolio.
- Bonds: Bonds, a safer investment compared to stocks, offer regular income through interest payments. Consequently, they remain a favored choice for generating retirement income.
- Mutual funds: Mutual funds allow investors to access diversified portfolios comprising stocks, bonds, or other assets. Individuals seeking a hands-off investment approach can find mutual funds appealing by engaging in professional management.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Resembling mutual funds but tradable like stocks, ETFs provide diversification and generally offer cost-effective solutions.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs enable individuals to invest in property without directly owning it. They provide a consistent income stream and potential capital appreciation.
Choosing the Right Mix of Investments
An appropriate blend of investments, commonly called asset allocation, is pivotal in retirement planning strategies. Here are key considerations to guide decision-making:
- Assess Your Risk Tolerance: Assessing one’s comfort level with investment risk is crucial. Risk-averse individuals may prefer low-risk options such as bonds, while those with higher risk tolerance may opt for more stocks in their portfolio.
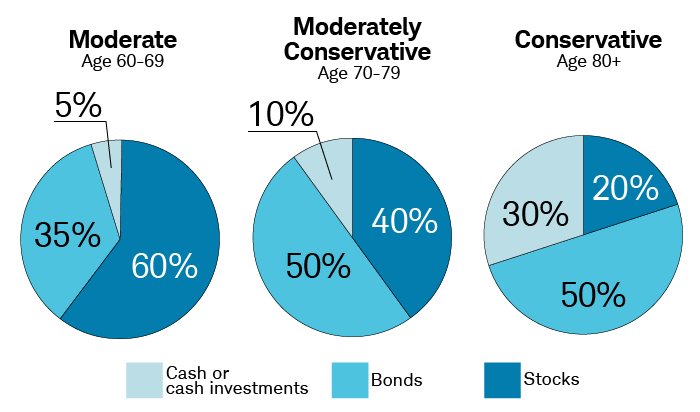
- Consider Your Retirement Timeline: Considering the distance to retirement is vital. Younger individuals can afford higher risk for potentially more significant returns, gradually transitioning to more conservative investments as retirement approaches, safeguarding their capital.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Diversification serves as a critical risk management strategy. Spreading investments across various asset classes mitigates the potential impact of substantial losses in any one sector.
- Regularly Review and Rebalance Your Portfolio: Over time, certain investments may outperform others, potentially disrupting the portfolio’s balance. Regular review and rebalancing ensure adherence to the desired asset allocation.
It is essential to remember that retirement planning strategies are not universally applicable. Customizing investment approaches to align with individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and retirement timeline is crucial. Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can provide valuable insights, helping individuals make informed investment decisions and stay on track with their retirement planning.
Credit: schwab.com
Frequently Asked Questions on Retirement Planning
When can you retire?
This question depends heavily on individual finances, well-being, and objectives. Nevertheless, 62 is the minimum age to claim Social Security benefits. When a person is 67, they are entitled to complete Social Security benefits. Savings and income are more important factors than age in determining retirement.
What is the necessary amount of money for retirement?
The money needed for a comfortable retirement relies on one’s present income, expenses, and how these may change post-retirement. A commonly used guideline aims to replace 70% to 90% of the annual pre-retirement income through savings and Social Security. As an example, if the average annual income is $63,000 before retirement, the annual income in retirement should range from $44,000 to $57,000. Individuals’ retirement income needs vary, however.
How to prioritize financial goals?
The prioritization of financial goals holds significant importance within retirement planning. While saving for retirement is crucial, other urgent financial goals may include debt repayment and establishing an emergency fund. Striking a balance is often the most effective approach. For instance, if an employer offers a retirement plan with matching contributions, it is advisable to contribute enough to receive the full match while simultaneously addressing other financial goals.
What are the best retirement plans?
Numerous retirement plans exist, and the most fitting one depends on individual circumstances. Plans sponsored by employers, such as 401(ks), make a great starting point, especially if companies match contributions. For those without access to employer-sponsored plans, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and Roth IRAs are also good options. Before choosing a plan, it’s important to understand its regulations and tax advantages thoroughly.
How to select retirement investments?
Selecting the optimal mix of investments constitutes a crucial component of retirement planning strategies. Investment choices should be based on risk tolerance, investment timeline, and financial objectives. Typically, younger investors can afford to assume more significant risks for the potential of higher returns, while individuals nearing retirement may prefer a more conservative investment approach. Additionally, diversification—spreading investments across various asset classes—is an essential strategy for risk management.





